Many passive fire protection products are claimed to be intumescent. What does this mean and when can a product be classed as intumescent?
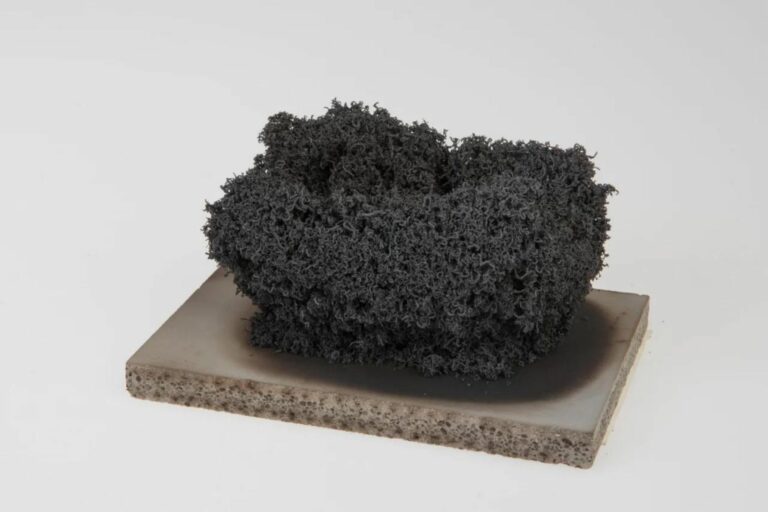
An intumescent is a substance that swells as a result of heat exposure, thus increasing in volume and decreasing in density. Intumescent materials used in fire protection will increase their volume significantly under the influence of heat (typically at 300°C – 500°C).
This physical process is one of the main principles for passive fire protection products. Intumescent sealants are able to close gaps in and around service penetration seals very quickly in the event that a fire occurs.
These are particularly useful for sealing around any combustible service pipes – which can melt and create larger openings in the building floors and walls – an important role in passive fire protection.
However, not all passive fire protection products are intumescent; for instance flexible silicone joint sealants, acrylic sealants, and some coated insulation boards are used for passive fire protection based on different chemical and/or physical principles.
Unfortunately, at this time, there is no clear definition of how much a material or product has to expand under heat in order to be classed as intumescent. This means that building owners and their professional construction team must take steps to check and confirm that the intumescent materials, systems, and products selected and used, will perform and that their volume will expand sufficiently to seal the dimensions of any openings and gaps that could be created during a fire.
Highly intumescent, fire resistance wrap before (left) and after (right) exposure to heat.